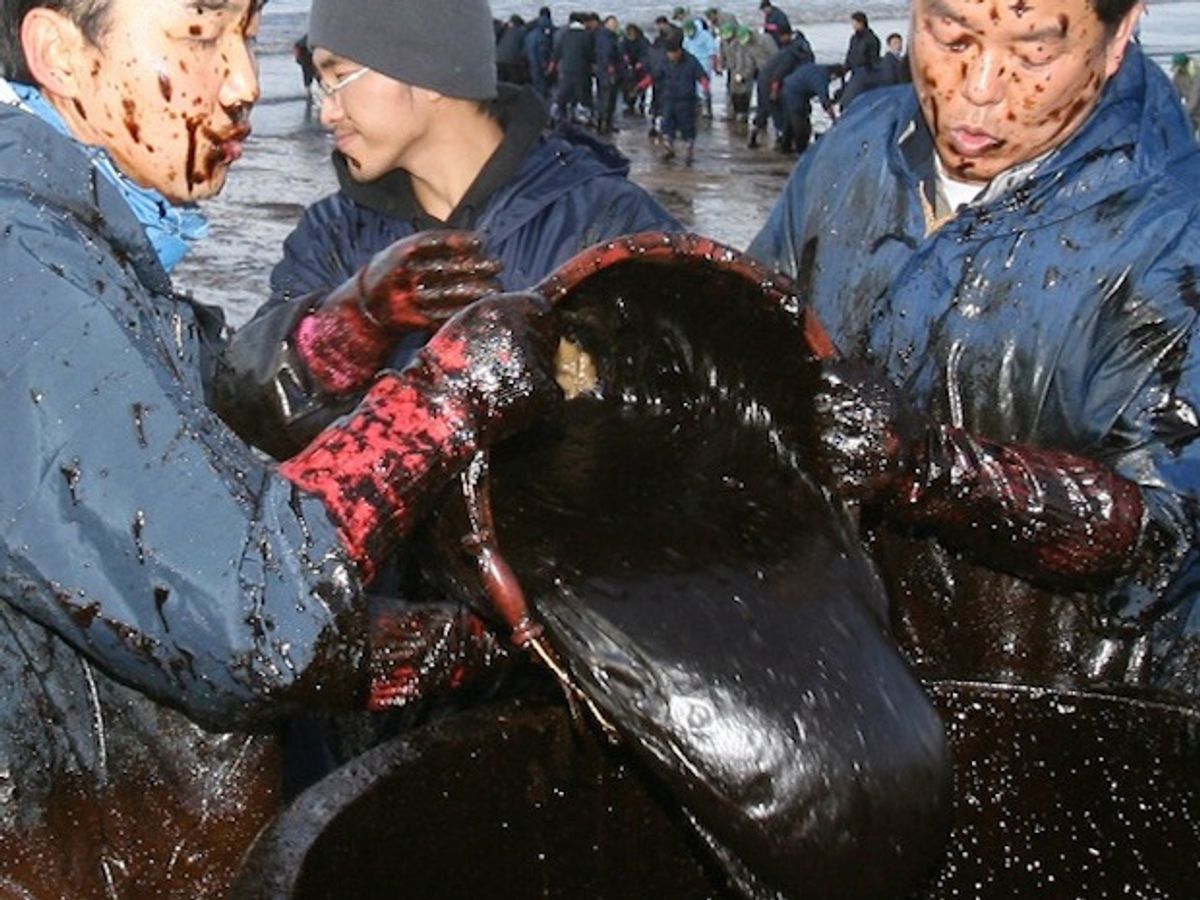
This blog has chronicled many nanomaterials suggested for cleaning up oil spills over the years, with the most recent being an aerogel developed in China that the researchers claim to be the lightest ever produced and capable of soaking up a rather astounding 900 times its own weight in oil. This compares favorably to the current mainstay for oil spill remediation, hay, which only absorbs 3 to 15 times its weight in oil.
Notable among them is that once the nanosheets have soaked up their share of oil, they can be cleaned and ready to be used again by merely letting them heat in ambient air for two hours. They also are hydrophobic, meaning they repel water, which allows them to float on the surface of the water and be available for easy retrieval during a clean up.
The nanosheets, which are fully described in the journal Nature Communications (“Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning”), were fabricated by mixing boron oxide powder and guanidine hydrochloride with methane and then heated at 1100 C for several hours in nitrogen gas. In this process, the guanidine hydrochloride decomposes to release several gasses that tunnel out, which results in the formation of the holes in the nanosheets.
So it sounds like a solution to oil spills is at hand—in fact, the Deakin University nanosheets have attractive characteristics for not just oil spill remediation but water purification in general. In fact, there are a variety of nanomaterials for these applications—so many of them that there are catalogues to guide you through them. But not so fast. As yet, no one is bothering to commercialize them so that they are available for the next oil spill.
Today is three years to the day since I first highlighted this critical point that the nanotechnologies exist but not the commercial interest in making them available for the next oil spill, not much has changed. Perhaps the only way to ensure that these superior technologies are available to clean up the next inevitable oil spill is to institute government regulations requiring them, as IEEE Spectrum editor, Steven Cherry, suggested on his podcast, also nearly three years ago. Sometimes you have to force markets to adopt technologies when doing so may not help the bottom line, but keeps our planet habitable.
Image: Weiwei Lei
Dexter Johnson is a contributing editor at IEEE Spectrum, with a focus on nanotechnology.