Conventional neuroprosthetic devices that aim to help patients bypass nerve damage are often rigid and power hungry. Now scientists have developed stretchable artificial nerves that helped paralyzed mice run on a treadmill and kick a ball while consuming less than one-hundredth of the power of a typical microprocessor. The scientists suggest these artificial nerves may one day be used in the human body.
To help restore movement to patients who have suffered nerve damage from injuries or diseases, scientists are researching neuroprosthetic devices that can help relay signals from the brain to muscles or nerves. However, these systems often face a number of critical limitations, says study co–senior author Tae-Woo Lee, a materials scientist at Seoul National University.
For example, conventional neuroprosthetic systems often depend on power-hungry external computing systems. They also typically stimulate the body with electric pulses of constant strength that abruptly increase and decrease in magnitude, “which cause drastic contraction of muscles that make patients uncomfortable,” Lee says.
To help generate more natural, comfortable movements, conventional neuroprosthetic systems may add voltage ramping during the start and end of electrical stimulation. However, this involves additional devices known as function generators that are typically rigid and bulky, Lee says, making them a poor fit for the human body.
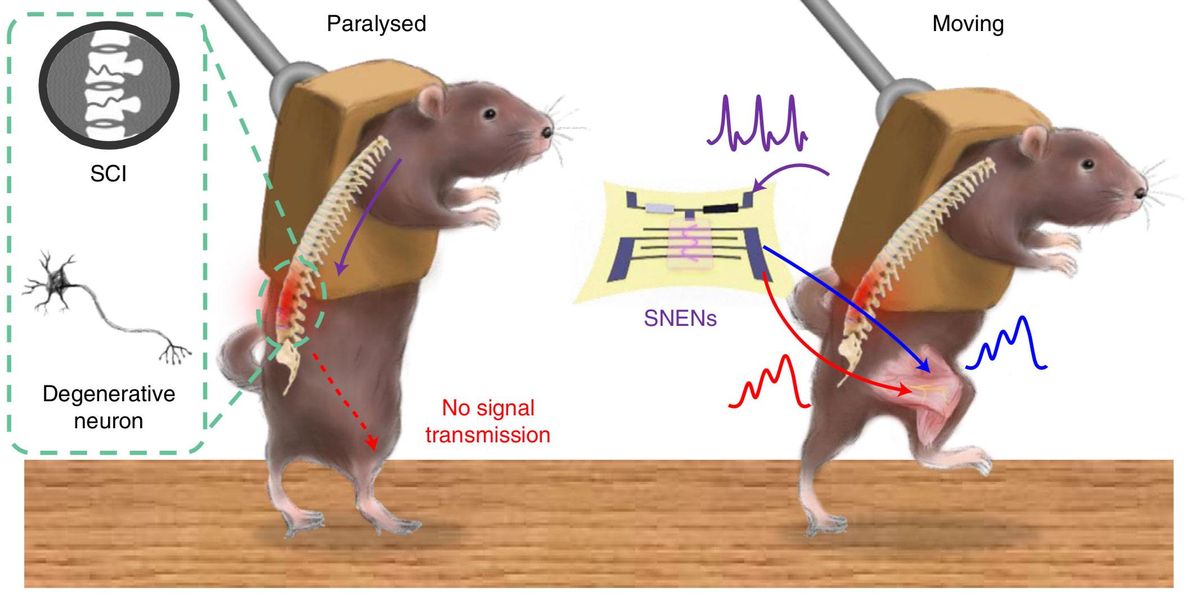
In the new study, the researchers developed highly stretchable electronic nerves that mimic real nerves. Like real nerves, these artificial nerves can deliver electric signals that gradually ramp up and down in strength. These artificial neuroprosthetics also consume only about 1/150 of the power of a typical microprocessor.
The new device consists of a stretchable organic semiconducting nanowire transistor that electrically stimulates muscles using soft, elastic hydrogel electrodes. This bioinspired or “biomimetic” device acts like an artificial synapse, a junction that links neurons together in the human body.
The device is coupled via an ion gel to a carbon nanotube sensor that detects strain. This serves as an artificial version of a proprioceptor, a sensor that receives signals from within the body to help it keep track of its position and movements. The researchers used this artificial proprioceptor to give real-time feedback to the electronic nerve. This helped keep the artificial nerve from overstimulating and overstraining mouse leg muscles, all without the need of external computers to control the movements.
In the new study, the researchers experimented with mice they anesthetized to paralyze their muscles in order to mimic injuries or diseases targeting nerves. They found they could use their artificial nerves and proprioceptors to generate coordinated smooth leg movements, including walking and running on a treadmill or kicking a ball. They also showed they could use the neuroprosthetics to move the legs of the mice with electrical signals recorded from the rodents’ brains.
“Our work is the first example of delivering biological neural signals through biomimetic electronic nerves to biological organs,” Lee says. “Through this, it seems possible to present new solutions and strategies for nerve damage in humans such as spinal-cord injury, peripheral nerve damage, and neurological damage such as Lou Gehrig’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease.”
In addition to potential medical applications, “the source technology of the stretchable artificial nerve may be applied to various medical wearable technologies,” says study co–senior author Zhenan Bao, a materials chemist at Stanford University, in California.
The scientists detailed their findings online 15 August in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.
- Their Bionic Eyes Are Now Obsolete and Unsupported - IEEE ... ›
- How Do Neural Implants Work? - IEEE Spectrum ›
- Brain Implants and Wearables Let Paralyzed People Move Again ... ›
- Researchers Teaching Robots to Feel and React to Pain - IEEE ... ›
- The Vagus Nerve: A Back Door for Brain Hacking - IEEE Spectrum ›
- Rerouting Intention And Sensation In Paralyzed Patients - IEEE Spectrum ›
Charles Q. Choi is a science reporter who contributes regularly to IEEE Spectrum. He has written for Scientific American, The New York Times, Wired, and Science, among others.