UPDATE 29 March 2024: “There’s still wide recognition [in China] that maintaining quantum capability is really strategically important, and there is still a desire to move it forward.” So said research associate Sam Howell from the Center for a New American Security last month as one of the quoted sources in an analysis by IEEE Spectrumon the somewhat confusing state of the quantum computer race in early 2024. Because two of the world’s biggest tech companies—the Chinese tech giants Alibaba and Baidu—have more or less cashed in on their stakes and appear to have left quantum computing behind. Which might suggest a change in the prevailing winds over this emerging technology.
But, said Edward Parker, professor of policy analysis at the RAND Corporation, in public testimony on Capitol Hill in Washington, D.C. in February, quantum computing remains a known disruptive tech that is nevertheless still emerging on the world’s stage. As he noted, at this early stage “the United States and China are each other’s largest scientific collaborators.” So while Beijing’s specific designs on quantum technology remain inscrutable—other than generic statements of its significance by China’s leaders—the research phase of this work still seems to be afoot. Parker said the country’s “single most important research institution” in quantum technologies today is based at the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei. Which, given that both cutting-edge quantum computers discussed below from three years ago originated at that institution, suggests that maybe even in an industry marked by rapid change, some things seem to be holding more or less steady as she goes. —IEEE Spectrum
Original story from 6 Nov. 2021 follows:
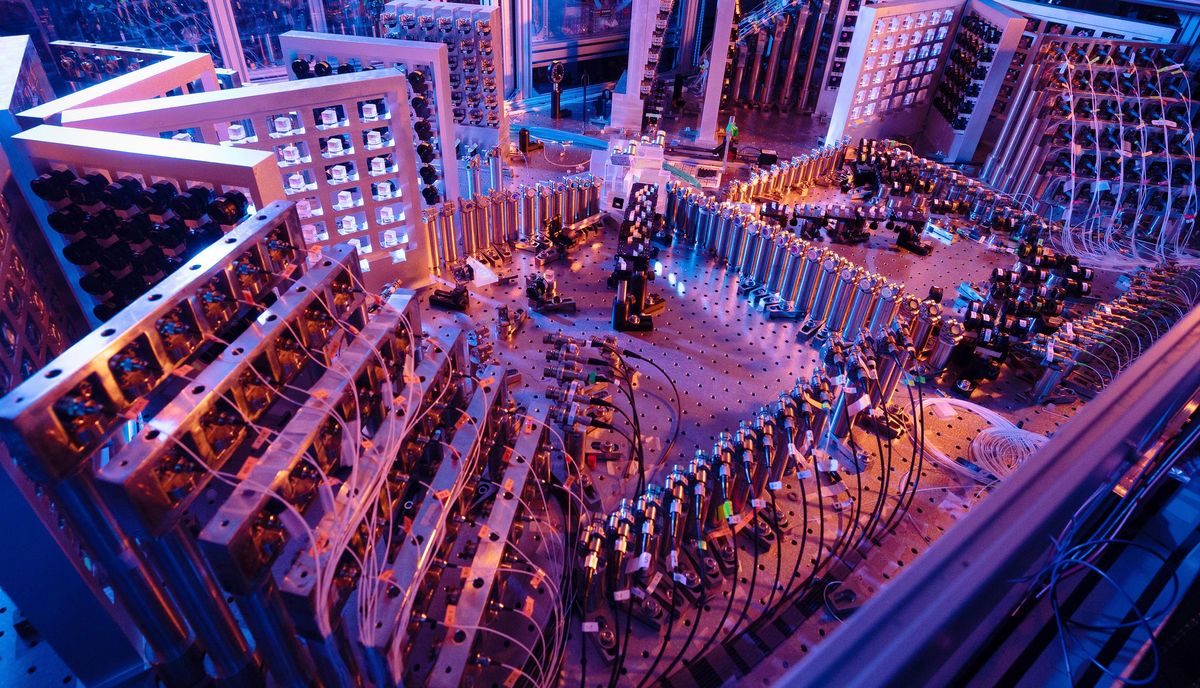
Two of the most powerful quantum computers in the world to date now both come from China, and new experiments with them re-ignite the controversy over what kinds of problems might be quantum computationally solvable that couldn’t begin to be solved by a conventional supercomputer.
A quantum computer with great enough complexity—for instance, enough components known as quantum bits or “qubits”—could in theory achieve a “quantum advantage“ allowing it to find the answers to problems no classical computer could ever solve. In principle, a quantum computer with 300 qubits could perform more calculations in an instant than there are atoms in the visible universe.
In 2019, Google argued it displayed such “quantum primacy“ with its 53-qubit Sycamore processor, carrying out a calculation in 200 seconds that the company estimated would take Summit, the world’s most powerful supercomputer at that time, 10,000 years. However, IBM researchers later called that quantum advantage claim in question, arguing that with better classical algorithms, Summit could actually solve that problem in 2.5 days.
“The current state of the art is that no experiments have demonstrated quantum advantage for practical tasks yet.” —Chao-Yang Lu, The University of Science and Technology of China
Now scientists in China have tested two different quantum computers on what they say are more challenging tasks than Sycamore faced and showed faster results. They note their work points to “an unambiguous quantum computational advantage.”
In one study, the researchers experimented with Zuchongzi, which used 56 superconducting qubits on a task whose solutions are random instances, or samples, from a given spread of probabilities. They found Zuchongzi completed such a sampling task in 1.2 hours, one they estimated would take Summit at least 8.2 years to finish. They also noted this sampling task was tens to hundreds of times more computationally demanding than what Google used to establish quantum advantage with Sycamore.
In another study, the scientists tested Jiuzhang 2.0, a photonic quantum computer, using Gaussian boson sampling, a task where the machine analyzes random patches of data. Using 113 detected photons, they estimated Jiuzhang 2.0 could solve the problem roughly 1024 faster than classical supercomputers.
Although the sampling task used in experiments with Zuchongzi has no known practical value, the Gaussian boson sampling problem on which Jiuzhang 2.0 was tested potentially has many practical applications, such as identifying which pairs of molecules are the best fits for each other. As such, this work may have quantum chemistry applications in simulating vital molecules and chemical reactions, says physicist Chao-Yang Lu at the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, a co-author on both studies.
These new experiments are “solid and necessary steps toward building increasingly advanced quantum computers,” Lu notes. But he also cautions against the increasing hype surrounding quantum computing.
“So far, the computational problems that can truly benefit from quantum computing are still quite limited,” Lu says. “The current state of the art is that no experiments have demonstrated quantum advantage for practical tasks yet. While we should not be too pessimistic and short-sighted as ‘the world needs only five quantum computers,’ we should also make a difference between optimism and exaggeration.”
The scientists detailed their findings Oct. 25 in two studies in the journal Physical Review Letters.
- Competing Visions Underpin China's Quantum Computer Race ... ›
- The Case Against Quantum Computing - IEEE Spectrum ›
- Recordbreaking Photonic Quantum Computer Comes From a Startup ›
- Alibaba and Baidu Cash Out on Quantum Computing Stakes - IEEE Spectrum ›
Charles Q. Choi is a science reporter who contributes regularly to IEEE Spectrum. He has written for Scientific American, The New York Times, Wired, and Science, among others.