As if it’s not hard enough to make very small mobile robots, once you’ve gotten the power and autonomy all figured out (good luck with that), your robot isn’t going to be all that useful unless it can carry some payload. And the payload that everybody wants robots to carry is a camera, which is of course a relatively big, heavy, power hungry payload. Great, just great.
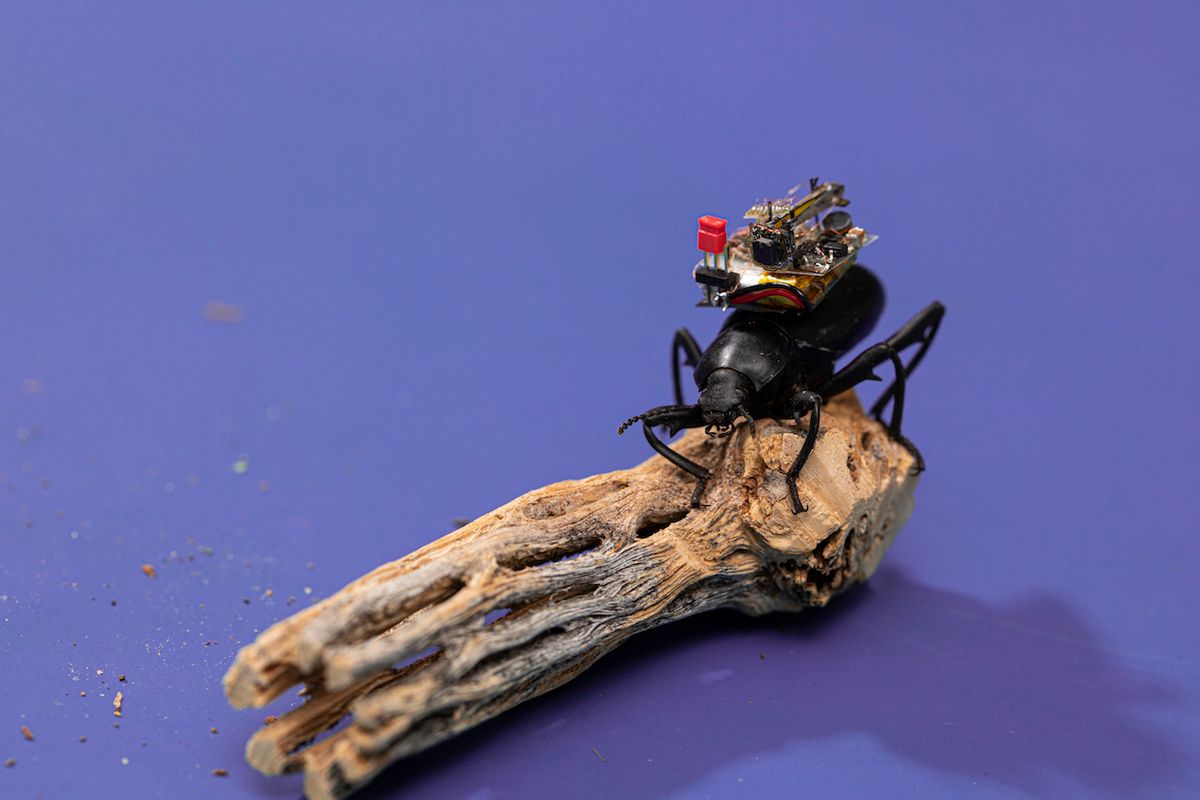
This whole thing is frustrating because tiny, lightweight, power efficient vision systems are all around us. Literally, all around us right this second, stuffed into the heads of insects. We can’t make anything quite that brilliant (yet), but roboticists from the University of Washington, in Seattle, have gotten us a bit closer, with the smallest wireless, steerable video camera we’ve ever seen—small enough to fit on the back of a microbot, or even a live bug.
To make a camera this small, the UW researchers, led by Shyam Gollakota, a professor of computer science and engineering, had to start nearly from scratch, primarily because existing systems aren’t nearly so constrained by power availability. Even things like swallowable pill cameras require batteries that weigh more than a gram, but only power the camera for under half an hour. With a focus on small size and efficiency, they started with an off-the-shelf ultra low-power image sensor that’s 2.3 mm wide and weighs 6.7 mg. They stuck on a Bluetooth 5.0 chip (3 mm wide, 6.8 mg), and had a fun time connecting those two things together without any intermediary hardware to broadcast the camera output. A functional wireless camera also requires a lens (20 mg) and an antenna, which is just 5 mm of wire. An accelerometer is useful so that insect motion can be used to trigger the camera, minimizing the redundant frames that you’d get from a robot or an insect taking a nap.

The last bit to make up this system is a mechanically steerable “head,” weighing 35 mg and bringing the total weight of the wireless camera system to 84 mg. If the look of the little piezoelectric actuator seems familiar, you have very good eyes because it’s tiny, and also, it’s the same kind of piezoelectric actuator that the folks at UW use to power their itty bitty flying robots. It’s got a 60-degree panning range, but also requires a 96 mg boost converter to function, which is a huge investment in size and weight just to be able to point the camera a little bit. But overall, the researchers say that this pays off, because not having to turn the entire robot (or insect) when you want to look around reduces the energy consumption of the system as a whole by a factor of up to 84 (!).

This efficiency means that the wireless camera system can stream video frames (160x120 pixels monochrome) to a cell phone up to 120 meters away for up to 6 hours when powered by a 0.5-g, 10-mAh battery. A live, first-bug view can be streamed at up to 5 frames per second. The system was successfully tested on a pair of darkling beetles that were allowed to roam freely outdoors, and the researchers noted that they could also mount it on spiders or moths, or anything else that could handle the payload. (The researchers removed the electronics from the insects after the experiments and observed no noticeable adverse effects on their behavior.)
The researchers are already thinking about what it might take to put a wireless camera system on something that flies, and it’s not going to be easy—a bumblebee can only carry between 100 and 200 mg. The power system is the primary limitation here, but it might be possible to use a solar cell to cut down on battery requirements. And the camera itself could be scaled down as well, by using a completely custom sensor and a different type of lens. The other thing to consider is that with a long-range wireless link and a vision system, it’s possible to add sophisticated vision-based autonomy to tiny robots by doing the computation remotely. So, next time you see something scuttling across the ground, give it another look, because it might be looking right back at you.
“Wireless steerable vision for live insects and insect-scale robots,” by Vikram Iyer, Ali Najafi, Johannes James, Sawyer Fuller, and Shyamnath Gollakota from the University of Washington, is published in Science Robotics.
Evan Ackerman is a senior editor at IEEE Spectrum. Since 2007, he has written over 6,000 articles on robotics and technology. He has a degree in Martian geology and is excellent at playing bagpipes.